Analysis of financial feasibility installing parking meters in Gianyar Regency (case study: Jalan Ngurah Rai – Gianyar)
Keywords:
financial feasibility, parking characteristics, parking metersAbstract
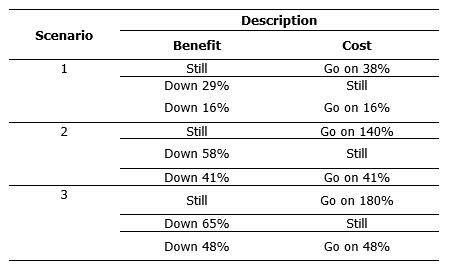
The increase in the number of motorized vehicles in Gianyar Regency has an impact on parking needs, as is the case on Jalan Ngurah Rai, Gianyar Regency. The data used in this research includes primary data obtained through parking inventory surveys, parking patrol surveys, and secondary data in the form of parking PD income data, parking meter price data, obtained from the Gianyar Regency Transportation Service. Parking characteristics for motorcycles are: parking inventory 95 SRP, parking volume in the 14-hour survey was 2147 vehicles, parking duration was 0.9318 hours, the parking capacity is 102 vehicles/hour, the parking provision is 1356 vehicles, and the parking index is 1,148. Parking characteristics for light vehicles are: parking inventory 88 SRP, parking volume in the 14-hour survey was 837 vehicles, parking duration was 1.0182 hours, the parking capacity is 85 vehicles/hour, the parking provision is 1128 vehicles, and the parking index is 0.92. The financial feasibility analysis for scenario 1 (fixed rate LV= 2000/one parking, MC= 1000/one parking) it is obtained that NPV = 3,153,280,747 > 0, BCR = 1,634 > 1, and IRR = 51% > MARR= 20%. For scenario 2 (fixed parking rate, LV=3000/hour, MC= 2000/hour) we get NPV = 8,998,418,237 > 0, BCR = 2,810 > 1, and IRR = 136%> MARR= 20%. For scenario 3 (fixed parking rate, first hour LV= 3000, MC= 2000, 1 hour later increase in LV= 2000/hour, MC= 1000/hour) obtained NPV = 11,625,402,449 > 0, BCR= 3,338 > 1, and IRR= 174%> MARR= 20%.
Downloads